TDS Information
What Are Total Dissolved Solids?
Total Dissolved Solids are the total weight of all solids that are dissolved in a given volume of water, expressed in units of mg per unit volume of water (mg/L), also referred to as parts per million.
'Dissolved solids' refer to any minerals, salts, metals, cations or anions dissolved in water. This includes anything present in water other than the pure water (H20) molecule and suspended solids. Suspended solids are any particles/substances that are neither dissolved nor settled in the water, such as wood pulp.
In general, the total dissolved solids concentration is the sum of the cations (positively charged) and anions (negatively charged) ions in the water.
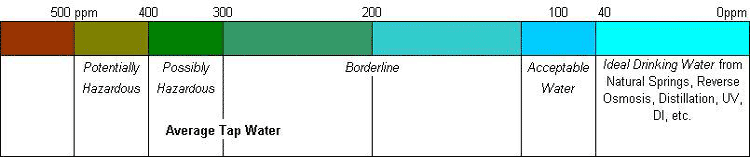
Parts per Million (ppm) is the weight-to-weight ratio of any ion to water. p>
Conductivity is usually about 100 times the total cations or anions expressed as equivalents. Total dissolved solids (TDS) in ppm usually ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 times the electrical conductivity.
Why Should You Measure the TDS level in your Water?
Water with a high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) count of over 50 ppm becomes electrically charged and can actually conduct an electric current. Such water will actually cause a small electric light bulb to become illuminated, and of course, will also conduct excessive charges of electricity throughout the body.
High total dissolved solids may affect the aesthetic quality of the water, interfere with washing clothes and corroding plumbing fixtures. For aesthetic reasons, a limit of 500 mg/l (milligrams per litre) has been established as part of the Secondary Drinking Water Standards. (EPA)